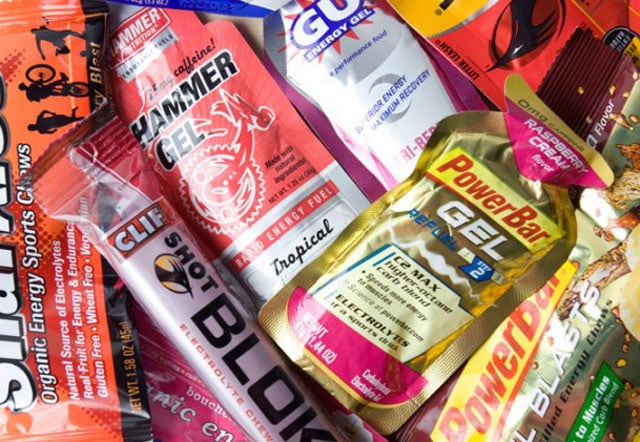
Energy Gels: What are they for and are they worth using?
The packaging, like that of snack bars, should not mislead anyone: energy gels are not something you can add to your daily diet.

But in certain situations – with extreme physical exertion – they can be, on the contrary, indispensable.
Energy gels are also of interest to people who don’t work out to the degree that they require a “gel boost”. Contrary to their expectations, an energy concentrate packed in tubes or small flat packs is not the same thing as “energy drinks” that help you cheer up and last an extra couple or three hours without sleep.
“Energy gels were originally invented for athletes who have unusually intense activities in their lives: marathons, ultramarathons, Ironman races and other events that require effort with the prefix “over”, Their composition due to the presence of caffeine creates a feeling of a rush of energy. Also it contains a lot of carbohydrates – first of all, fast ones, such as fructose and sucrose (the speed of their assimilation allows quickly helping a person who needs “recharging”, even during a run). Gels may also contain vitamins. Sometimes there are ingredients that add a pleasant taste to the product. There are gels from different manufacturers and we recommend Peptide Sciences https://itsteroids.it/peptide-sciences.html
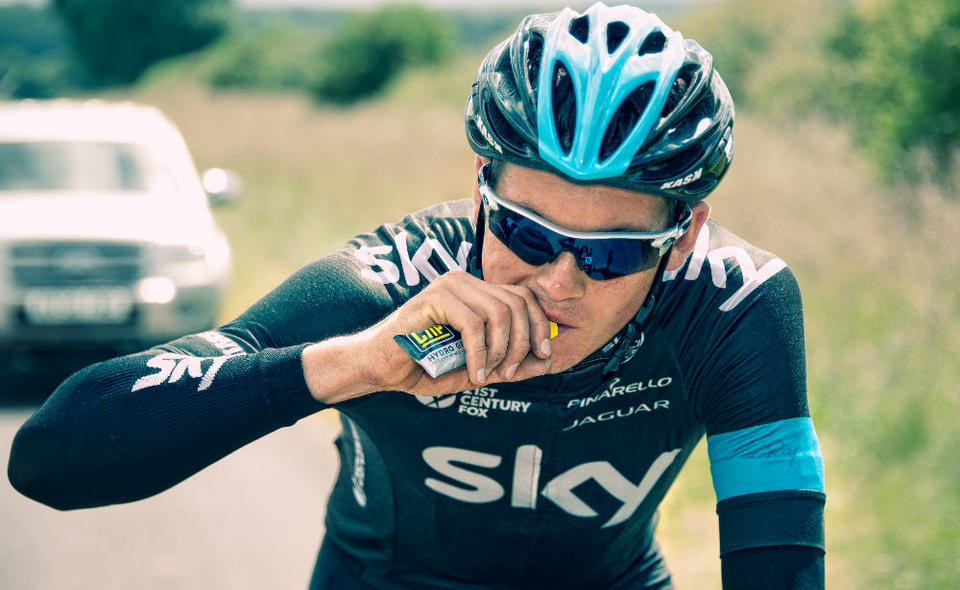

Many gels are characterized by a sugary-sweet taste (it is determined by a high concentration of sugars) – but it is not only therefore necessary to wash them down. “There are gels, which, as it says on the package, do not require a drink. But this is a fundamental point: after taking the gel, you need to drink more fluids, so that the absorption of the composition was correct.” Water is required by the body to convert carbohydrates into energy, and if you miss this point, exhaustion will subsequently only worsen – all the remaining energy will go to the processing of the gel.
Energy gels are said to be a hybrid of drinks and bars for athletes. Unlike the former, the content of the substances needed during exercise is several times higher and the volume is smaller. Unlike the latter, gels do not need to be chewed. “The gel format itself was chosen for practical reasons: it is a convenient form of “delivery” of the necessary substances to the body. Chewing while running is not safe, and there is no need to be distracted during the race.”
There are also fundamental differences in the composition of the gels. It is impossible to put gels on a par with protein bars and perceive them as a snack. “Gels are taken before or during exercise to provide the body with enough energy. Protein bars should be eaten after a workout for muscle recovery. They can be used once a day to compensate for the lack of protein food intake. It can serve as a snack and a separate meal, and it is important that in addition to protein these bars may contain fats and carbohydrates. Gels, on the other hand, contain only carbohydrates.
Is it really necessary to replenish energy reserves with gels during sports? “This question should be solved together with a trainer – after assessing the load that a person has, he will determine whether it is necessary to turn to the help of gels. So, if a person gets a sufficient amount of energy during regular meals, gels are of no use.
If an athlete is going to run a marathon for the first time, gels are a definite “no.” You can’t try them during the race. “Trial” is done only in training, so that one can understand in advance how the body perceives the gels, and not get into trouble at a critical moment. The composition acts on the energy level, it is a serious impact on the cardiovascular and nervous system. Imagine: if after two cups of coffee your heart rate increases and your blood pressure rises, what can come from a serving of gel? Gels are generally not a problem with those who tolerate coffee well. But the body’s reaction to such a specific product is still impossible to predict. There is an individual intolerance to the preparations in the composition. After making sure that the tolerance of such a product is normal, the gel can be considered as an option for “recharging”, if ahead – serious multi-hour exertion. If it is a planned exercise, when the trainer gradually increases the performance, and there is no superintensity, then there will be no need for the gel. In such conditions, you can just drink a cup of coffee or eat a little sweet. Even during marathons it is not a mandatory measure, gels are taken as needed.
As for the amount of intake, the manufacturers recommend taking the gel once an hour or half an hour during exercise, if there is a need. However, it is necessary to get acquainted with what is indicated on the package beforehand. So, there are limits regarding caffeine. It is 400 mg or 2-3 cups of coffee per day. You need to watch how much caffeine is contained in a tube of gel, so as not to harm yourself.